-
How we help
- Does my software work?
- Does it work for all users?
- Global Growth Toolbox
- Industries
-
Platform
- Platform
- Integrations
- Browse all test types
- Add-on services
- Pricing
- Resources
Usability testing guide | What is it? How do I get started?
Usability testing is extremely beneficial for your product; but very tricky to get right. This page will give you everything you need to get started with usability testing.
How can you ensure your product provides the best possible user experience? Usability testing offers the answer. When you observe how real users interact with your app, website, or prototype, you can uncover insights that lead to more intuitive and user-friendly designs.
In this blog post, we'll dive into the benefits of usability testing, the various methods available, and how to use them to improve your product's overall usability.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a process where you evaluate how easy it is for people to use a product. This involves observing whether the product's design meets users' expectations and allows them to interact with it efficiently and effectively.
What is the purpose of a Usability Test?
Gathering user feedback is crucial in designing a product that meets their expectations. Whether it's an object we use daily, like a remote control or kitchen blender, or a digital format like a website, or mobile app, it must align with users' natural instincts when navigating and using it. This way, we can create an optimal user experience that satisfies their needs and preferences.
Usability testing helps ensure this alignment, and the process is often simpler than you might anticipate.
Usability testing vs. User testing vs. UX testing
User testing, UX testing, and usability testing assess how users interact with a product, but they focus on different aspects. Usability testing is a more specific type of testing that checks how easily users can use a product. It focuses on non-functional issues that could prevent users from completing tasks effectively.
UX testing, or user experience testing, is broader and encompasses usability testing. It includes any test that affects the overall user experience. While it might gather a lot of feedback for the product team, not all of it will relate directly to usability issues unless it affects users' success with the product. User testing is the broadest term and involves testing on users. It covers functionality, content, and aesthetics – in addition to usability. User testing can also include various methods beyond the structured experiments associated with usability testing.
Example
Here's an example to illustrate these differences using a new fitness-tracking app:
- Usability testing assesses how easily users can log workouts, set goals, and track progress. It looks for obstacles, like confusing buttons or unclear instructions, that may hinder users' ability to complete tasks.
- UX testing, beyond usability, also checks the app's rewards system, the interface's intuitiveness, and the overall appeal of the design and color scheme. This feedback helps improve the app's emotional impact and visual aesthetics.
- User testing tests the app's overall performance, including how well it syncs with wearable devices and the clarity of instructional content. This includes various methods, such as surveys and interviews, to gain comprehensive feedback on functionality, content, and aesthetics.
Why should you undertake Usability Tests?
There are many different reasons for undertaking usability tests. For example:
1. Increased user success = more money!
It is important to identify usability issues mainly for commercial reasons. Improving usability can lead to better commercial performance, and research by the NN group has found a 135% return on investment in usability.
Usability impacts all product usage and growth aspects, making it a crucial factor for success. When users are more satisfied with a product, they are more likely to continue to use it, leave positive reviews, and recommend it to others, leading to more signups.
2. Pinpoint problem areas
Usability testing helps identify problem areas by observing real users interacting with a product. It reveals where users struggle, encounter confusion, or make errors while completing tasks.
Through participant feedback, task success rates, and behavioral observations, usability tests pinpoint specific user interface design, navigation, content clarity, and functionality issues. This firsthand insight allows designers and developers to address these problems, ultimately improving the user experience and ensuring the product better aligns with user needs and expectations.
3. Drive user-centered design
Engaging real users ensures products are designed based on actual needs and preferences. Testing uncovers user pain points, preferences, and behaviors, providing valuable insights for design improvements.
Usability testing fosters a deep understanding of user perspectives, ensuring that the final product aligns with user expectations, resulting in higher user satisfaction and successful user-centered design.
4. Preventing expensive dev work
Identifying usability issues as early as possible in the product process can be useful in preventing software with usability issues from reaching production.
When should you conduct Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a versatile method that can be applied at any point in the design or development process. You can perform usability tests on early-stage design prototypes and use the results to inform future designs, as well as test later-stage products such as live websites or apps.
To achieve the best results, consider conducting multiple rounds of usability testing throughout development. This iterative approach allows you to identify and address usability issues early on, providing ample time for adjustments.
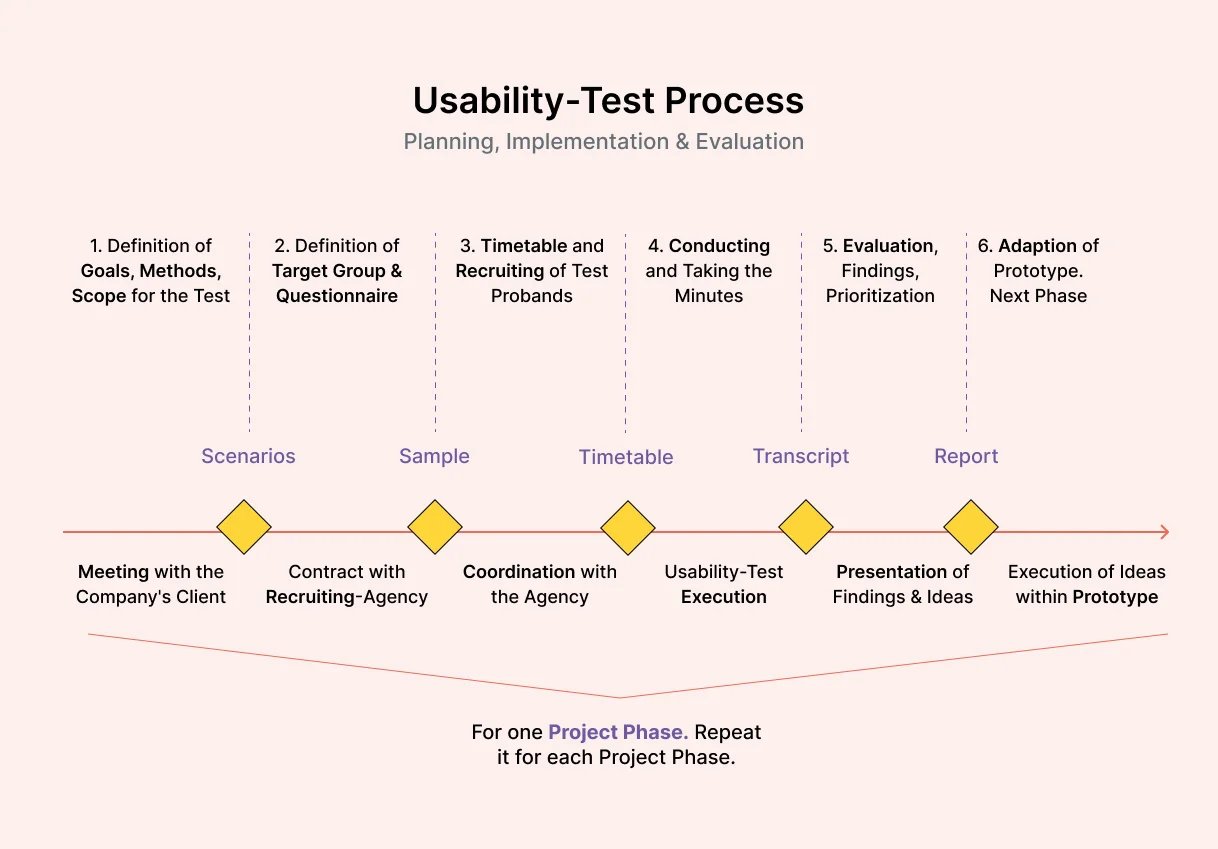
Begin by creating a usability testing plan to establish when you'll conduct tests during the process. Here are some common phases for testing the usability of products:
- Prototyping phase: Testing during this phase can prevent costly issues down the line. Conduct usability tests on interactive prototypes before development begins to ensure user-friendly designs and smooth functionality from the outset.
- Pre-launch: As your product nears completion, conduct a final round of usability testing to optimize user satisfaction and eliminate any remaining issues. Test complex user flows and observe how focus groups interact with the product to gather valuable insights.
- Before a redesign: When considering a redesign, usability testing helps identify what needs improvement in the existing design. Gather feedback from potential customers to understand the design's shortcomings and gather suggestions for the new iteration.
- Regular checks: Conduct regular usability testing sessions, such as every six months, to keep up with changing user expectations and industry trends. Also, test major design changes to ensure they enhance the user experience rather than detract from it.
Who conducts Usability Testing?
Ideally, someone with experience in UX design should lead the test, but you can also conduct the testing yourself. To do this, you need:
- The product (let's use the example of a new smartphone)
- A video recorder
- A microphone, and
- A list of tasks.
Designers, developers, project managers, and CEOs can all conduct usability tests. Additionally, some companies, like Global App Testing, offer remote, moderated testing services if you wish to outsource these tasks.

4 steps to conduct Usability Testing
1. Identify users:
Try to recruit participants who are representative of your target audience. Though this isn't strictly necessary, it can provide more relevant insights. Typically, testing with five users is sufficient.
2. Design tasks:
Create specific tasks for users to perform with the product. These tasks should be clear and focused on the actions you want to test. For example, you might ask users to set up the new smartphone, take a photo, and share it with friends. This way, you can see if they can efficiently complete the tasks without confusion. Avoid leading questions or suggestive prompts, as they can introduce bias. The goal is to observe how a user naturally interacts with the product.
3. Conduct the testing:
Prepare your testing environment with your materials, find a quiet space, and offer snacks for participants. Invite observers like managers and executives to watch the testing sessions live. Seeing how one person interacts with the product is often eye-opening.
4. Analyze the results:
After testing, review the data and summarize the findings. Focus on users' feedback and the challenges they encountered. Organize the results in a simple bulleted list for clarity. If there are many issues to address, prioritize them based on importance.
Practical Usability Testing scenarios for product improvement
Let's have a closer look at some usability testing scenarios for different products:
1. Identify points of friction
Scenario: If you have a new home appliance such as a smart oven, usability testing might reveal that users struggle with setting cooking times or adjusting the temperature. Observing users and gathering their feedback can help you identify these points of friction and adjust the user interface or controls to make the process smoother.
2. Stress test across many environments
Scenario: Testing a fitness tracker with different users in various environments (e.g., outdoor running, indoor cycling) can expose issues such as inaccurate step counts or GPS tracking problems. Testing under different conditions helps uncover bugs you may not have seen in controlled testing.
3. Provide diverse perspectives from your user base
Scenario: If you are testing a language learning app, having users with different native languages participate can reveal usability issues in translation accuracy or cultural context. Their feedback can guide you in refining your app's language options and instructions.
4. Give clear insights into the product's strengths and weaknesses
Scenario: For a productivity tool, usability testing can show you how your software stacks up against competitors. Users might praise the ease of creating tasks but struggle with organizing them, indicating where you can enhance features or improve the interface.
5. Inspire future additions or enhancements
Scenario: In the case of a meal delivery app, usability testing may uncover user requests for more dietary filters or more specific meal customization options. These insights can guide future iterations and enhancements to meet customer demands and improve overall satisfaction.
Types of Usability Testing
Although there are more than 10 ways to perform usability testing, let's go over the broader categorization. Usability testing can take two primary forms:
Qualitative Usability Testing: This approach gathers insights and observations about how users interact with a product or service. It's useful for identifying issues within the user experience and is more commonly used than quantitative testing.
Quantitative Usability Testing: This approach gathers measurable data to describe the user experience, such as task success rates and completion times. It's effective for establishing benchmarks and assessing performance.
The ideal number of participants for a usability test depends on the study type. For most qualitative studies with a single user group, five participants typically suffice to identify the majority of common problems.
Remote vs. In-person Testing
Remote usability tests have gained popularity due to their cost and time efficiency compared to in-person studies. There are two main types:
- Remote moderated Usability Testing: This resembles in-person testing, with a facilitator guiding participants through tasks. However, the facilitator and participant are in different locations, often using screen-sharing software such as Zoom or Skype.
- Remote unmoderated Usability Testing: Participants complete tasks independently at their convenience using a dedicated online testing platform. The researcher sets up the tasks and follow-up questions and then reviews session recordings and metrics, such as task success rates, once the participant finishes the test.
Choosing and monitoring test metrics
You're almost ready to begin your usability testing initiative. Well done! Your hard work and planning have brought you to this point. Now, you need to think about how you'll monitor your testing session and what metrics you'll use.
There are three main types of usability testing metrics:
- Effectiveness metrics: Measure how successful users are at completing tasks.
- Efficiency metrics: Evaluate how quickly users can complete tasks.
- Satisfaction metrics: Assess how users feel about the overall experience.
Using a mix of these metric types is a good idea to get a comprehensive view of any usability problems across the user experience.
Some top metrics to consider include:
- Task success: The percentage of users who successfully complete tasks.
- Number of errors: The number of mistakes users make during task completion.
- Time on task: How long it takes participants to complete a task.
- Single Ease Question (SEQ): Measures how easy users find a task on a scale of 1-7.
- Subjective Mental Effort Question (SMEQ): Measures how challenging users found a task.
- Confidence: Users rate their confidence in task completion on a scale of 1-7.
- SUM: A combined metric that includes task success, ease of use, and time on task.
When choosing and monitoring test metrics, you'll want to include:
- Plan ID: Unique identifier for your test plan.
- Goal: The main objective of the test.
- Summary: Brief overview of the test.
- Timeline and dates: Key dates for your testing.
- Investment: Budget and resources allocated to the test.
- Scope of test: Features and areas to be tested, along with any exclusions.
- Device and version approach: Details about the hardware and software involved.
- Methodology: The specific approach you'll use for the test.
- Participant profile: Description of the test participants.
- Observation criteria: What will you be observing during the test?
- Interview questions: Questions you'll ask participants.
- Coordinated dependencies and responsibilities: Team members and their roles.
- Worksheet: A document to track your observations.
- Expected method of analysis: How you'll analyze the data collected.
- Hypothesis: What do you expect the test results to show?
How can Global App Testing help with Usability Testing?
Global App Testing offers usability and UX testing services that can significantly benefit businesses looking to improve the user experience of their applications.
Here's how we can help:
- Comprehensive test coverage: We provide thorough testing across 6,000 devices, operating systems, and regions to ensure your app works seamlessly for all users, regardless of their location or setup.
- Real-world testing: We use real-world scenarios and environments to test your app, providing insights into how actual users interact with your product.
- Rapid feedback: Our network of testers allows us to provide quick feedback on usability and UX issues – in 48 hours or less!
- Experienced testers: Expertise of over 90,000 ensures the testing process is thorough and effective.
- Actionable insights: We provide detailed reports and insights on usability issues and user feedback to help you better understand areas for improvement.
- Flexibility and scalability: Our testing services can be customized to your needs and scale with your project.
- Multilingual testing: We ensure your app is usable and accessible to users around the world.
- Cross-platform testing: Test your app across various platforms, including web, mobile, and desktop, to ensure a consistent user experience across all devices.
- Remote testing: Our remote testing capabilities allow you to access a global pool of testers and receive feedback without the need for in-person testing sessions.
Partner with Global App Testing to improve your app's usability and user experience. Contact us now for a customized testing plan and take your app to the next level!
FAQ
What is 'The rule of 5' in Usability Testing?
The rule of 5 in usability testing is a cost-effective approach that involves testing with just five participants. According to the Nielsen Norman Group, using five people allows you to uncover almost as many usability issues as you would with a larger group of participants. This method strikes a balance between efficiency and effectiveness.
What are usability test tools?
Usability test tools are software solutions that help you evaluate the usability and intuitiveness of your designs. These tools enable you to observe how users interact with your prototype, website, or application and whether they can successfully complete tasks. By providing insights into user behavior and feedback, usability testing tools allow you to enhance your user experience and design products that meet user needs and expectations.
What is a good usability score?
A good usability score is determined using the System Usability Scale (SUS), which ranges from 0 to 100. A perfect score of 100 indicates flawless usability and an exceptional user experience. The average SUS score is 68, and scores up to 70% are generally seen as good, indicating a decent level of usability.
Keep learning
Top 10 Mobile Usability Testing Methods You Should Know
A guide to outsourced software testing
Software localization challenges and solutions[Guide]
Need help with QA testing?
We’d love to give you a personal demo of our platform. Find out how we manage, execute and analyse test results to help you release high quality software anywhere in the world.

